Indulge in the yummy world of the science of ice cream. We’ll uncover the secrets behind this adored frozen treat. From its humble beginnings to its wide array of flavors, ice cream has delighted taste buds for centuries. Let’s dive deep into the sweet science of ice cream.
Discover how ice cream has advanced since ancient times when frozen treats were enjoyed by royalty and nobility. We’ll journey through time revealing the fascinating facts and stories that have shaped this cool delight.
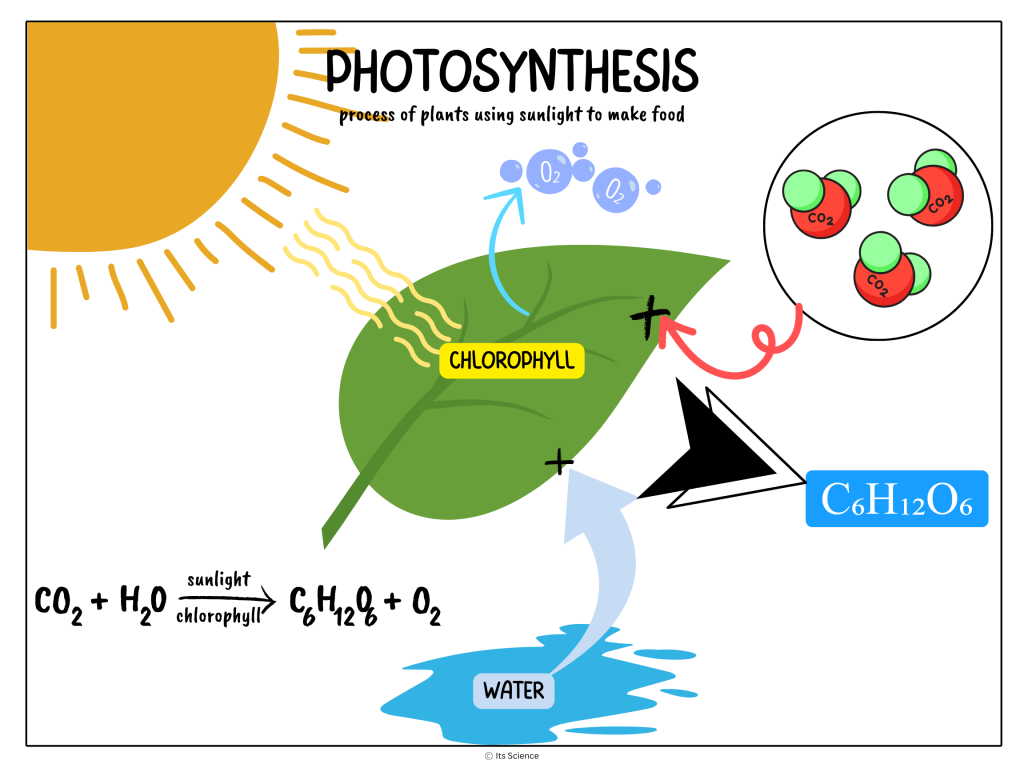
Learn about the science of ice cream, from the fine balance of sugar and cream to the role of air in creating a creamy texture. We’ll also explore the secrets of flavoring, including the use of natural ingredients and special techniques that add richness and complexity to every scoop.
So, whether you prefer vanilla and chocolate or crave combinations like salted caramel and lavender, join us as we uncover the mysteries and sheer joy of ice cream.
The History of Ice Cream
Ice cream traces its origins back to ancient civilizations. The Chinese were known to enjoy a frozen mixture of milk and rice as early as 200 BC. Ancient Rome, while not enjoying a milky version, made frozen sweets from a mix of snow and ice with fruit juices, honey, and other flavorings to create early forms of frozen treats. Wealthy Romans sent slaves to gather ice and snow which was then stored in pits covered with straw and other materials to preserve the ice in warmer months.
After the fall of the Roman Empire, the practice of enjoying frozen desserts continued in various forms throughout the Middle Ages. The Arabs improved upon the concept by introducing milk-based recipes, which laid the foundation for modern ice cream.
In the Middle Ages, Marco Polo brought the concept of ice cream to Europe after discovering it during his travels in the East. However, it was not until the 17th century that ice cream gained popularity among the elite in Europe, with recipes including cream and sugar.
In the Renaissance period, particularly in Italy, chefs began to experiment with frozen desserts. The Medici family in Florence is known to have enjoyed a dessert resembling sorbet, and Catherine de’ Medici is credited with bringing these recipes to France when she married Henry II. As the centuries passed, ice cream became more accessible to the general population.
The hand-cranked ice cream churn was invented by Nancy Johnson, an American, in 1843. Her invention significantly advanced the process of making ice cream, making it more accessible and easier to produce at home.
Ice cream has also played a role in various historical events. George Washington, the first President of the United States, had a well-documented fondness for ice cream. His enthusiasm for the treat played a notable role in the early history of ice cream in America.
Also, Thomas Jefferson is said to have written down one of the first American ice cream recipes. Some of the popular and evolving flavors were tomato, vanilla, coffee, chocolate, burnt almond, lemon, nutmeg, and oyster. Later, in World War II, ice cream became a symbol of American resilience, with soldiers craving the taste of home while stationed abroad.
Popular Ice Cream Flavors Around the World
One of the joys of ice cream is the vast array of flavors available to tease your taste buds. While classics like vanilla, chocolate, and strawberry remain all-time favorites, different regions have their signature flavors that reflect local tastes and ingredients. In Italy, gelato prevails, with flavors like pistachio, hazelnut, and stracciatella being popular choices.
In Japan, unique flavors such as matcha green tea, black sesame, and sweet potato are highly sought after. In India, traditional flavors like mango, saffron, and cardamom add a touch of exoticism to ice cream offerings. South American countries like Brazil and Argentina are known for their creamy flavors like dulce de leche and passion fruit.
The United States boasts a diverse range of ice cream flavors, with quirky combinations like bacon and maple syrup, avocado, and even beer-flavored ice cream. Whether you prefer classic flavors or want to step out of your comfort zone, there’s an ice cream flavor out there for everyone.
The Science of Ice Cream: Making It
At its core, ice cream is a delicate balance of fat, sugar, and air. The key to achieving that creamy texture lies in the proper proportion of these ingredients. The cream provides richness, sugar adds sweetness, and helps lower the freezing point, while air incorporated during the churning process creates a light and airy consistency.
The process of making ice cream involves lowering the temperature of the mixture to freeze it slowly. The ice crystals need to form evenly to give the dessert a smooth texture. The use of stabilizers like egg yolks or gelatin can also help prevent ice crystals from forming too quickly and make for a creamier end product.
Flavoring ice cream is an art in itself. Natural ingredients like fruits, nuts, and spices are commonly used to infuse ice cream with unique flavors. Extracts, essences, and flavorings can also be added to enhance the taste profile. Some modern techniques involve infusing flavors through sous vide (under vacuum) or using liquid nitrogen for instant freezing, creating a velvety texture and intense flavors.
The Role of Ingredients in Creating the Perfect Ice Cream
The quality of ingredients can greatly impact the final product. Plus, it plays a key role in the science of ice cream. Fresh dairy products like milk, cream, and eggs are essential for a rich and creamy base. Choosing high-quality vanilla beans, cocoa powder, or fresh fruits also increases its excellence.
Sugar is not only a sweetener but also plays a crucial role in the texture of ice cream. It helps lower the freezing point of the mixture, preventing it from turning into a solid block of ice. But, it takes just the right amount as too much sugar can make the ice cream overly sweet and soft. Balancing the sweetness with the other ingredients is key.
Emulsifiers like lecithin or stabilizers like guar gum are often added to ice cream to improve its texture and prevent it from melting too quickly. These ingredients help emulsify the fats and water in the mixture, resulting in a smoother and more stable ice cream.
Tips for Making Homemade Ice Cream
Making ice cream at home is a fun and tastefully rewarding experience. With just a few simple ingredients and some patience, you can create delicious ice cream right in your kitchen (or science classroom/ creating lab activities). Start by choosing a base recipe that suits your taste preferences.
Invest in a good ice cream maker to ensure that your ice cream freezes evenly and churns to the right consistency. Pre-chill the mixture before pouring it into the ice cream maker to speed up the freezing process. Experiment with different flavor combinations by adding mix-ins like chocolate chips, nuts, or cookies.
To prevent ice crystals from forming, store your homemade ice cream in an airtight container and press a piece of wax paper or plastic wrap directly onto the surface before sealing. This helps create a barrier against air exposure, maintaining the ice cream’s texture and flavor.
The Health Benefits of Ice Cream
While ice cream is often viewed as a self-indulgent treat, it does offer some surprising health benefits when consumed in moderation. Here health and the science of ice cream overlap.
Dairy-based ice cream is a good source of calcium, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. It also provides protein and vitamins like A, B12, and D, which support overall health.
Some studies suggest that the fats in ice cream can help the body absorb certain nutrients more effectively. However, ice cream made with natural ingredients and without excessive added sugars or artificial flavors is your best choice. Opting for frozen yogurt or sorbet can also reduce the calorie and fat content.
Ice cream can also be a mood booster. Surprise! Indulging in a scoop of your favorite ice cream can lift your spirits and provide a moment of comfort and pleasure. Just remember to enjoy it in moderation as part of a balanced diet to gain the benefits without overindulging.
Ice Cream Trends and Innovations
As consumer tastes and culinary trends change, the world of ice cream continues to evolve and surprise with new flavors and techniques. From plant-based milk alternatives to artisanal small-batch productions, there’s a growing emphasis on creativity and innovations in the ice cream industry.
Plant-based ice creams made from coconut, almond, or cashew milk have gained popularity among vegans and those with dietary restrictions. These dairy-free alternatives offer a creamy texture and rich flavor without undermining taste. Here too, the science of ice cream creation is necessary.
Small-scale ice cream makers are experimenting with unique ingredients like heirloom fruits, single-origin chocolate, and locally sourced honey to create one-of-a-kind flavors.
Sustainability is also a key focus for many ice cream brands, with a push towards eco-friendly packaging, fair trade ingredients, and reducing food waste. Some companies are using surplus ingredients like spent grain from brewing or imperfect fruits to create innovative ice cream flavors that benefit the environment and support local farmers.
Conclusion
From its ancient origins to its modern-day reinventions, it’s clear that the science of ice cream was and is important for making this confectionary treat. The variety of flavors, textures, and experiences that ice cream offers make it a universal delight that brings joy to all people of all ages.
As you explore the world of ice cream, from classic flavors to pioneering creations, remember to savor each scoop and appreciate the craftsmanship and artistry that goes into making this frozen dessert. Whether you’re enjoying a cone on a summer day or sampling exotic flavors in a new city, ice cream has the power to transport you to a place of pure happiness and joy.
So, treat yourself to a scoop of your favorite flavor, experiment with homemade recipes, or seek out diverse ice cream shops. The science of ice cream is as close as your nearest dairy freezer. So, embrace the creamy, dreamy world of ice cream and let your taste buds celebrate all the goodness this frozen delight has to offer. After all, life is too short not to enjoy a little scoop of happiness.
I scream. You scream. We all scream for… well, you know. Here is a great way to integrate a phase change lab activity with your study of matter (phase and physical changes of matter)… the Ice Cream Lab Activity. This is a favorite of students and teachers alike. [Click the image to find out more]

FREE Science Classroom Concept Posters
Click to learn more.