Introduction
Are you enthralled by the mention of chocolate? Do you crave its delicious taste and comforting effects? If so, read on as we uncover the science of chocolate and the brain.
From ancient civilizations that considered chocolate a gift from the gods to modern-day chocoholics, the allure of chocolate spans centuries and cultures.
Locked within this delightful treat are a host of compounds that influence brain function.
Let’s delve into delve into the science of chocolate’s effects on the brain and explore the key components responsible for its cognitive and emotional benefits. Understanding this relationship, you can indulge in your favorite treat with a deeper appreciation for its powerful impact on your mind.
The Composition of Chocolate

Chocolate’s core ingredients are simple, yet, profound: cocoa solids, cocoa butter, sugar, and milk. The amounts of each create the rich, complex flavors and textures we associate with chocolate.
Cocoa solids, derived from the cacao bean, are packed with chemical compounds that offer both taste and health benefits. Cocoa butter is the natural fat extracted from the beans. This butter gives chocolate its smooth, melt-in-your-mouth quality. While the sugar and milk add sweetness and creaminess, needed to balance the intensity of the cocoa and strengthen the overall sensory experience. Each ingredient plays an essential role in the final product, influencing not only taste but also the potential health benefits.
Dark chocolate contains the highest percentage of cocoa solids and cocoa butter. With little to no milk, the results are a more intense and slightly bitter flavor. The dark type is often highlighted for its health benefits due to the higher concentration of cocoa-derived compounds.
Milk chocolate, on the other hand, has a lower cocoa content due to milk solids. The addition of dairy products gives this chocolate a creamier texture and sweeter taste.
White chocolate contains no cocoa solids at all. It is made using only cocoa butter, sugar, and milk. This is why some would say that it isn’t true chocolate.
Each type of chocolate offers a unique profile of ingredients and flavors. And, each type caters to various choices and dietary needs.
The key chemicals in the science of chocolate that affect the brain compounds are flavonoids, theobromine, caffeine, and phenylethylamine.
Flavonoids, found in abundance in dark chocolate, are powerful antioxidants that have been linked to improved brain function and reduced risk of neurologic diseases.
Theobromine and caffeine are stimulants that enhance alertness and cognitive performance.
Phenylethylamine, often referred to as the “love drug,” can influence mood and emotional well-being.
Working together these compounds offer both immediate and long-term benefits for brain health, which makes chocolate not just a treat for the taste buds but also a potential boost for mental and emotional wellbeing.
Flavonoids: The Antioxidant Powerhouse
Flavonoids, in the science of chocolate, are a group of naturally occurring compounds found in various fruits, vegetables, and cocoa beans. Flavanols, a type of flavonoid, are particularly abundant in chocolate. These flavanols are responsible for chocolate’s antioxidant properties, which help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. The presence of flavanols in chocolate is a key factor in that it exalts chocolate from a mere indulgence to a food with potential health benefits.
Understanding the science of chocolate involves exploring how flavonoids act as antioxidants and their role in brain health. As you may know, antioxidants are vital in neutralizing free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and diseases.
Flavonoids in chocolate help protect brain cells from free radical damage, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative conditions. Additionally, flavonoids promote the production of nitric oxide which improves blood flow and oxygen levels to the brain. This increased circulation supports overall brain function, including memory, focus, and mental abilities.
Studies in the science of chocolate have linked flavonoid consumption to improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of neurological disease. Research has shown that regular intake of flavonoid-rich foods, such as dark chocolate, can lead to better performance on cognitive tests, improved memory, and slower age-related mental decline.
Some studies suggest that flavonoids may help in reducing the risk of diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by protecting nerve cells and supporting brain plasticity. These findings highlight the potential of flavonoids in chocolate to contribute not only to immediate brain function but also to long-term mental health. These findings make chocolate a delicious and beneficial addition to a balanced diet.
Theobromine and Caffeine: The Stimulants
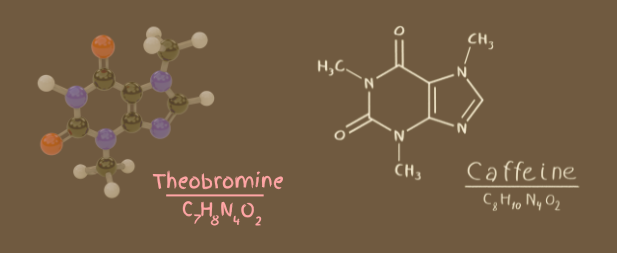
The science of chocolate also reveals the significant roles of theobromine and caffeine as key stimulants in chocolate. Theobromine is a naturally occurring compound in cocoa beans. It has a chemical structure similar to caffeine. While both theobromine and caffeine belong to a class of chemicals called methylxanthine, theobromine has a milder stimulating effect compared to caffeine. This subtle difference means theobromine gives gentle stimulation without the intense jolt often associated with caffeine. These stimulants are crucial in explaining why chocolate can give us that delightful boost in energy and alertness.
Delving into the science of chocolate, we see that theobromine and caffeine affect the central nervous system. Theobromine works by stimulating the heart, dilating blood vessels, and relaxing smooth muscles. This leads to a feeling of increased energy and well-being. Caffeine, on the other hand, works by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain. This action prevents drowsiness and promotes wakefulness. Together, these compounds influence various aspects of brain function, including improved concentration, increased alertness, and faster reaction times. These stimulating effects are why many people reach for chocolate when they need a quick mental lift.
The combined impact of theobromine and caffeine in chocolate on alertness, mood, and cognitive performance is well-documented in the science of chocolate. Studies have shown that these stimulants can improve mood by increasing the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are associated with pleasure and happiness.
Additionally, theobromine and caffeine working together can enhance cognitive performance, making tasks requiring mental effort seem less daunting. This synergistic effect contributes to the overall sense of well-being and mental sharpness experienced after consuming chocolate, making it not just a treat but a potential ally in maintaining mental health and emotional balance.
Phenylethylamine: The Love Drug
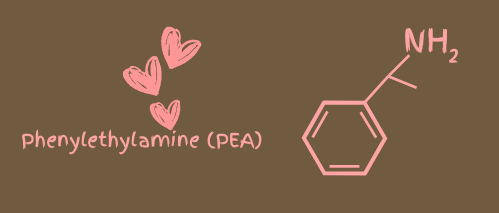
Phenylethylamine, in our looks at the science of chocolate, is often referred to as the “love drug”. PEA occurs naturally in cocoa beans and plays a significant role in the brain. Structurally similar to amphetamines, PEA acts as a central nervous system stimulant, although much milder. It’s known for its ability to elevate mood and induce feelings of pleasure and excitement. That is why it’s often associated with the sensation of being in love.
PEA stimulates the release of endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good chemicals. This can lead to heightened feelings of happiness and well-being. Additionally, PEA can enhance alertness and energy levels, giving one an overall uplifted mood. It’s this powerful mood-boosting effect that has earned PEA its nickname, “the love drug.” When you consume chocolate, the presence of PEA can mimic the euphoria experienced during romantic encounters, making chocolate a go-to comfort food for many.
The interaction of PEA with neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin is a crucial aspect of the science of chocolate. PEA will increase the levels of these neurotransmitters. That, in turn, works on regulating mood and emotional states.
Dopamine is associated with pleasure and reward, while serotonin contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness. So when PEA enhances their effects it improves mood, reduces stress, and promotes a sense of contentment. This biochemical interaction explains why chocolate can be so comforting and enjoyable.
Chocolate and Mood Enhancement

This science of chocolate provides strong evidence for chocolates’ ability to enhance mood. Chocolate consumption triggers the release of endorphins (natural painkillers) which give one a feeling of happiness and euphoria.
Additionally, chocolate stimulates the production of serotonin, which is known for its mood-regulating properties. Its biochemical reaction can help alleviate stress, anxiety, and depression, which is what makes chocolate a popular comfort food. Combine the pleasurable experience of eating chocolate with its biochemical effects, and you have a powerful mood-boosting combination that can enhance overall well-being.
The sensory pleasure of its rich, creamy texture and sweet taste can provide another sense of comfort and satisfaction. This psychological effect is why many people turn to chocolate during times of emotional distress or simply to treat themselves. The act of eating chocolate can also serve as a form of self-care. People use it as a reward or for relaxation on a busy day. Chocolate’s emotional connection adds another layer to its ability to improve mood and promote a positive mental state.
Long-term cognitive benefits are also part of the science of chocolate. Studies have investigated the potential protective effects of chocolate consumption against cognitive decline and dementia. Antioxidants and flavonoids in chocolate have been linked to improved brain health, enhancing memory, focus, and overall cognitive function. Regular consumption of flavonoid-rich dark chocolate has been associated with better cognitive performance and a lower risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases. The secret is to add moderate amounts of chocolate into a balanced diet to gain these long-term brain health pluses.
As with any food, the science of chocolate emphasizes the importance of moderation. While chocolate offers many health benefits, it is also high in sugar and calories. These calories can lead to negative health effects if taken in excess. Opt for healthier chocolate options, such as dark chocolate with a high cocoa content, which provides more of the beneficial compounds and less sugar.
By choosing high-quality, flavonoid-rich dark chocolate and enjoying it in moderation, you can harness its benefits without compromising your overall health. Remember to savor each bite and appreciate what makes chocolate a uniquely enjoyable treat.
Conclusion
The science of chocolate unveils a blend of benefits for both mood and brain health. By understanding the key compounds in chocolate—such as flavonoids, theobromine, caffeine, and phenylethylamine—we can appreciate how this beloved treat positively impacts our mental well-being.
From enhancing mood via endorphins and serotonin to providing long-term mental benefits through antioxidants, chocolate offers more than just an appealing taste. Its ability to improve alertness, mood, and cognitive performance makes it a valuable addition to a balanced diet when enjoyed mindfully and in moderation.
The science behind chocolate, added to your daily life, can be both enjoyable and helpful. Choosing high-quality dark chocolate with a high cocoa content ensures you get the maximum health benefits while minimizing sugar intake. To that, practice savoring each bite. In doing so, you will not only have the emotional, but physical pleasure from this delicious treat. Whether you indulge occasionally or include it as a regular treat, understanding the science of chocolate empowers you to make informed choices that enhance your overall quality of life.